Difference: HowToGuides (1 vs. 16)
Revision 162011-04-07 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
How-To Guides | ||||||||
| Line: 7 to 7 | ||||||||
Apr 6, 2011
Installing R and RServeInstalling R | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | see http://www.r-project.org/ | |||||||
Installing packages
| ||||||||
Revision 152011-04-07 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
How-To Guides | ||||||||
| Line: 6 to 6 | ||||||||
Using RApr 6, 2011Installing R and RServe | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | Installing RInstalling packages
| |||||||
Running RServesee http://rosuda.org/Rserve/doc.shtml | ||||||||
Revision 142011-04-06 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
How-To Guides | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | Using RApr 6, 2011Installing R and RServeRunning RServesee http://rosuda.org/Rserve/doc.shtml
| |||||||
Running ExperimentRunnerMar 28, 2011
| ||||||||
Revision 132011-03-28 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
How-To GuidesRunning ExperimentRunner | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Jan 28, 2011
| |||||||
| > > | Mar 28, 2011
| |||||||
| ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
| ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | These are all available from /ubc/cs/project/arrow/mavc/workspace/smac/ | |||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
| Line: 22 to 23 | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | create by running ExperimentRunner.java from Eclipse. Alternatively, run it from Eclipse.
| |||||||
| > > | create by running CmdLineExperimentRunner.java from Eclipse. Alternatively, run it from Eclipse with the appropriate Run Configuration.
| |||||||
Running Locally | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
Running on Arrow | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
Running on Westgrid
| ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||
| > > |
* setenv LD_LIBRARY_PATH
<MCR_ROOT>/bin/glnx86:
<MCR_ROOT>/sys/os/glnx86:
<MCR_ROOT>/sys/java/jre/glnx86/jre1.4.2/lib/i386/client:
<MCR_ROOT>/sys/java/jre/glnx86/jre1.4.2/lib/i386:
<MCR_ROOT>/sys/opengl/lib/glnx86:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
* setenv XAPPLRESDIR <MCR_ROOT>/X11/app-defaults | |||||||
Monitoring with Hal | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
| ||||||||
| Deleted: | ||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||
Westgrid Quick Start | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | Getting a Westgrid accountGetting files onto WestridSubmitting jobs to Westgrid | |||||||
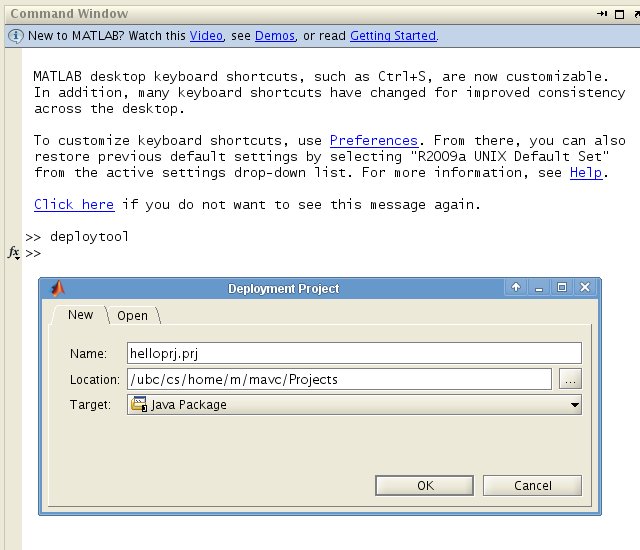
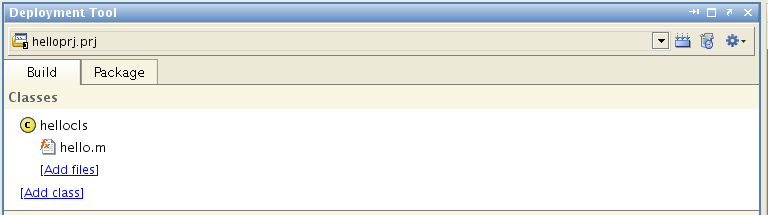
Matlab Builder JA Quick StartSee attached user guide | ||||||||
| Line: 90 to 106 | ||||||||
| Pass by reference is available with the MWJavaObjectRef wrapper, a subclass of MWArray. | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | HAL quick start guideversion 1.0b4 Nov. 29, 2010 NOTE: this quite is very much a work-in-progress. If you have any isses that aren't covered here, or any other comments or questions, please contact us at cnell@csDELETEthisTEXT.ubc.caSuper quick start (linux only):- download full HAL 1.0 zip distribution; install using below instructions. - download sample experiment package; import using the HAL 1.0 interface - try configuring, analysing the provided sample algorithm (SPEAR)HAL"> Installing HAL- download the full zip package - extract the zip to a working directory - double click the HAL_Basic configuration- after first start of HAL, a file called HAL.json will be created. Basic configuration settings can be modified by editing this file - RECOMMENDED: if you have a MySQL server, use it instead of the default SQLite database. To do so, edit the HAL.json file; change: "database":"jdbc:sqlite:hal.db" to something like "database":"jdbc:mysql://Plugin installation- to install a new HAL plugin, copy the plugin .jar file into the /plugins/ folder and restart HAL.Defining an algorithmTo add a new algorithm for use in HAL, use the "Define a new algorithm" wizard:Algorithm specification- The name+version combination must be unique in the database. - Supported instance tag sets are used to restrict which algorithms can be run on particular instances. A tag set such as {cnf, 3sat} marks the algorithm as compatible with any instance with both "cnf" and "3sat" tags. An algorithm can have multiple instance tag sets; at least one of them must be satisfied by an instance in order for it to be considered compatible. If no tags are specified, the HAL will assume the algorithm is compatible with all instances. - Advanced properties: deterministic: stgraightforward; note that if your algorithm has a seed as an input, mark it as NOT determinsitic, and explicitly identify the seed parameter (below). - Advanced properties: exportable: An algorithm is exportable if and only if HAL can compress the entire directory tree rooted at the executable file, exctract it on a different machine, and the algorithm will work on that second machine. - Advanced properties: cutoff-independence: Set this to true if the algorithm's behaviour will not change if cutoff inputs are changed but all other inputs remain the same. HAL uses this property to decide whether it can infer cutoffs or completions from previously-performed runs. - Executable: should be the first command to run the algorithm; if the algorithm is an interpreted script this might be "python" or "ruby". Note that this path must exist ON THE SYSTEM RUNNING HAL, not the system running the browser that is interfacing with HAL (if the two differ). - Command-line argument string: see example. Note that all input variables (specified like $name$ in the command string) will need to be further defined in later steps. (NOTE: HAL does not currently support generating input files for target algorithms.) - Algorithm output specification. Format is the same as the command-line argument specification; and as in that case, all identified output variables will require further specification. HAL will use this string to parse outputs from the standard output and error streams of the algorithm during execution.Identify configurable parameters:- a configurable parameter is a parameter whose value may be tuned by a configurator to optimize performance; all "other" settings will be left unchangedSpecify configurable parameter domains- for every input parameter marked as configurable, the domain of valid values must be specified. - conditionalities between parameters can be specified, where conditionality refers to "activation" of parameters. For example, parameter X can be marked as active only if parameter Y takes some particular value. - prohibited parameter configurations can similarly be specified. 3.4: as 3.3, for "other" input settings 3.5: as 3.3, for output variablesInstance set specificationTo specify an instance set, use the Create New InstanceDistribution wizard: - distirbution name must be unique - tags are used to filter compatible algorithms (see 3.1 above) - An instance is exportable if it is fully-defined by a single file - The directory path must be valid on the system runnign HAL, not the system running the web browser | |||||||
| > > | Javadoc Location | |||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | Turning off display.
| |||||||
| Deleted: | ||||||||
| < < | --- | |||||||
| Deleted: | ||||||||
| < < | Experiment specification- Metrics: PAR1 and PAR10 rely on HAL-measured CPU time; Reported PAR1 and PAR10 rely on algorithm-reported CPU time | |||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | HAL quick start guidesee http://hal.cs.ubc.ca/ | |||||||
| ||||||||
Revision 122011-02-05 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
How-To Guides | ||||||||
| Line: 6 to 6 | ||||||||
Running ExperimentRunnerJan 28, 2011
| ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | currently only located in the [smac working copy] branch. | |||||||
| > > | currently only located in the [smac working copy] branch. The files are also available from /ubc/cs/project/arrow/mavc/workspace/smac/ | |||||||
| ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
| ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | ||||||||
| > > | These are all available from /ubc/cs/project/arrow/mavc/workspace/smac/ | |||||||
| Line: 17 to 16 | ||||||||
| Deleted: | ||||||||
| < < | ||||||||
| | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
| ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | create by running ExperimentRunner.java from Eclipse. | |||||||
| > > | create by running ExperimentRunner.java from Eclipse. Alternatively, run it from Eclipse. | |||||||
| ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | ||||||||
Running Locally | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | ||||||||
Running on Arrow | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
Running on Westgrid | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
Monitoring with Hal
| ||||||||
Revision 112011-02-02 - mavc
Revision 102011-01-28 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
How-To Guides | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | Running ExperimentRunnerJan 28, 2011
Running LocallyRunning on ArrowRunning on WestgridMonitoring with Hal
| |||||||
Westgrid Quick StartMatlab Builder JA Quick Start | ||||||||
Revision 92011-01-15 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
How-To Guides | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | Westgrid Quick Start | |||||||
Matlab Builder JA Quick StartSee attached user guide | ||||||||
Revision 82011-01-14 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | HAL-related tutorialsThis page is the temporary home of HAL-related tutorials. | |||||||
| > > | How-To Guides | |||||||
Revision 72011-01-13 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
HAL-related tutorialsThis page is the temporary home of HAL-related tutorials. | ||||||||
| Deleted: | ||||||||
| < < | HA
| |||||||
Matlab Builder JA Quick StartSee attached user guide | ||||||||
| Line: 129 to 118 | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
Revision 62011-01-13 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
HAL-related tutorialsThis page is the temporary home of HAL-related tutorials. | ||||||||
| Line: 6 to 6 | ||||||||
HA
| ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
Installation and ConfigurationDefining a New Algorithm | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | HAL objects"> Saving and Loading HAL objects | |||||||
| > > | HAL obje"> Exporting and Importing HAL objects | |||||||
Matlab Builder JA Quick StartSee attached user guide | ||||||||
Revision 52011-01-11 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
HAL-related tutorialsThis page is the temporary home of HAL-related tutorials. | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | HA
| |||||||
Matlab Builder JA Quick StartSee attached user guideHello World | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | A trivial "Hello World" example is described below. We will describe how to call the following Matlab function from Java. | |||||||
| > > | A "Hello World" example is described below. We will describe how to call the following Matlab function from Java. | |||||||
| ||||||||
| Line: 26 to 37 | ||||||||
Calling code from Eclipse
| ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < |
Passing Data | |||||||
| > > |
Data Types and Conversion | |||||||
Data conversion classes are available in the following hierarchy:
| ||||||||
Revision 42011-01-10 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
HAL-related tutorialsThis page is the temporary home of HAL-related tutorials. | ||||||||
| Line: 27 to 27 | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Data Type ConversionData and FiguresProgramming Help | |||||||
| > > | Passing DataData conversion classes are available in the following hierarchy:
| |||||||
HAL quick start guideversion 1.0b4 Nov. 29, 2010 | ||||||||
Revision 32011-01-07 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
HAL-related tutorials | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | This page will contain HAL-related tutorials. | |||||||
| > > | This page is the temporary home of HAL-related tutorials. | |||||||
Revision 22011-01-06 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | HAL quick start guide | |||||||
| > > | HAL-related tutorialsThis page will contain HAL-related tutorials.Matlab Builder JA Quick StartSee attached user guideHello WorldA trivial "Hello World" example is described below. We will describe how to call the following Matlab function from Java.Exporting JAR
Calling code from Eclipse
Data Type ConversionData and FiguresProgramming HelpHAL quick start guide | |||||||
| version 1.0b4 Nov. 29, 2010 NOTE: this quite is very much a work-in-progress. If you have any isses that aren't covered here, or any other comments or questions, please contact us at cnell@csDELETEthisTEXT.ubc.ca | ||||||||
| Deleted: | ||||||||
| < < | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Super quick start (linux only): | |||||||
| > > | Super quick start (linux only): | |||||||
| - download full HAL 1.0 zip distribution; install using below instructions. - download sample experiment package; import using the HAL 1.0 interface - try configuring, analysing the provided sample algorithm (SPEAR) | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | HAL"> Installing HAL | |||||||
| > > | HAL"> Installing HAL | |||||||
| - download the full zip package
- extract the zip to a working directory
- double click the HAL_ | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Basic configuration | |||||||
| > > | Basic configuration | |||||||
| - after first start of HAL, a file called HAL.json will be created. Basic configuration settings can be modified by editing this file
- RECOMMENDED: if you have a MySQL server, use it instead of the default SQLite database. To do so, edit the HAL.json file; change:
"database":"jdbc:sqlite:hal.db" to something like "database":"jdbc:mysql:// | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Plugin installation | |||||||
| > > | Plugin installation | |||||||
| - to install a new HAL plugin, copy the plugin .jar file into the /plugins/ folder and restart HAL. | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Defining an algorithm | |||||||
| > > | Defining an algorithm | |||||||
| To add a new algorithm for use in HAL, use the "Define a new algorithm" wizard: | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Algorithm specification | |||||||
| > > | Algorithm specification | |||||||
| - The name+version combination must be unique in the database. - Supported instance tag sets are used to restrict which algorithms can be run on particular instances. A tag set such as {cnf, 3sat} marks the algorithm as compatible with any instance with both "cnf" and "3sat" tags. An algorithm can have multiple instance tag sets; at least one of them must be satisfied by an instance in order for it to be considered compatible. If no tags are specified, the HAL will assume the algorithm is compatible with all instances. - Advanced properties: deterministic: stgraightforward; note that if your algorithm has a seed as an input, mark it as NOT determinsitic, and explicitly identify the seed parameter (below). | ||||||||
| Line: 44 to 74 | ||||||||
| (NOTE: HAL does not currently support generating input files for target algorithms.) - Algorithm output specification. Format is the same as the command-line argument specification; and as in that case, all identified output variables will require further specification. HAL will use this string to parse outputs from the standard output and error streams of the algorithm during execution. | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Identify configurable parameters: | |||||||
| > > | Identify configurable parameters: | |||||||
| - a configurable parameter is a parameter whose value may be tuned by a configurator to optimize performance; all "other" settings will be left unchanged | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Specify configurable parameter domains | |||||||
| > > | Specify configurable parameter domains | |||||||
| - for every input parameter marked as configurable, the domain of valid values must be specified. - conditionalities between parameters can be specified, where conditionality refers to "activation" of parameters. For example, parameter X can be marked as active only if parameter Y takes some particular value. - prohibited parameter configurations can similarly be specified. | ||||||||
| Line: 58 to 88 | ||||||||
| 3.5: as 3.3, for output variables | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Instance set specification | |||||||
| > > | Instance set specification | |||||||
| To specify an instance set, use the Create New InstanceDistribution wizard: - distirbution name must be unique - tags are used to filter compatible algorithms (see 3.1 above) | ||||||||
| Line: 68 to 98 | ||||||||
| --- | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Experiment specification | |||||||
| > > | Experiment specification | |||||||
| - Metrics: PAR1 and PAR10 rely on HAL-measured CPU time; Reported PAR1 and PAR10 rely on algorithm-reported CPU time | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
Revision 12011-01-05 - mavc
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | HAL quick start guideversion 1.0b4 Nov. 29, 2010 NOTE: this quite is very much a work-in-progress. If you have any isses that aren't covered here, or any other comments or questions, please contact us at cnell@csDELETEthisTEXT.ubc.caSuper quick start (linux only):- download full HAL 1.0 zip distribution; install using below instructions. - download sample experiment package; import using the HAL 1.0 interface - try configuring, analysing the provided sample algorithm (SPEAR)HAL"> Installing HAL- download the full zip package - extract the zip to a working directory - double click the HAL_Basic configuration- after first start of HAL, a file called HAL.json will be created. Basic configuration settings can be modified by editing this file - RECOMMENDED: if you have a MySQL server, use it instead of the default SQLite database. To do so, edit the HAL.json file; change: "database":"jdbc:sqlite:hal.db" to something like "database":"jdbc:mysql://Plugin installation- to install a new HAL plugin, copy the plugin .jar file into the /plugins/ folder and restart HAL.Defining an algorithmTo add a new algorithm for use in HAL, use the "Define a new algorithm" wizard:Algorithm specification- The name+version combination must be unique in the database. - Supported instance tag sets are used to restrict which algorithms can be run on particular instances. A tag set such as {cnf, 3sat} marks the algorithm as compatible with any instance with both "cnf" and "3sat" tags. An algorithm can have multiple instance tag sets; at least one of them must be satisfied by an instance in order for it to be considered compatible. If no tags are specified, the HAL will assume the algorithm is compatible with all instances. - Advanced properties: deterministic: stgraightforward; note that if your algorithm has a seed as an input, mark it as NOT determinsitic, and explicitly identify the seed parameter (below). - Advanced properties: exportable: An algorithm is exportable if and only if HAL can compress the entire directory tree rooted at the executable file, exctract it on a different machine, and the algorithm will work on that second machine. - Advanced properties: cutoff-independence: Set this to true if the algorithm's behaviour will not change if cutoff inputs are changed but all other inputs remain the same. HAL uses this property to decide whether it can infer cutoffs or completions from previously-performed runs. - Executable: should be the first command to run the algorithm; if the algorithm is an interpreted script this might be "python" or "ruby". Note that this path must exist ON THE SYSTEM RUNNING HAL, not the system running the browser that is interfacing with HAL (if the two differ). - Command-line argument string: see example. Note that all input variables (specified like $name$ in the command string) will need to be further defined in later steps. (NOTE: HAL does not currently support generating input files for target algorithms.) - Algorithm output specification. Format is the same as the command-line argument specification; and as in that case, all identified output variables will require further specification. HAL will use this string to parse outputs from the standard output and error streams of the algorithm during execution.Identify configurable parameters:- a configurable parameter is a parameter whose value may be tuned by a configurator to optimize performance; all "other" settings will be left unchangedSpecify configurable parameter domains- for every input parameter marked as configurable, the domain of valid values must be specified. - conditionalities between parameters can be specified, where conditionality refers to "activation" of parameters. For example, parameter X can be marked as active only if parameter Y takes some particular value. - prohibited parameter configurations can similarly be specified. 3.4: as 3.3, for "other" input settings 3.5: as 3.3, for output variablesInstance set specificationTo specify an instance set, use the Create New InstanceDistribution wizard: - distirbution name must be unique - tags are used to filter compatible algorithms (see 3.1 above) - An instance is exportable if it is fully-defined by a single file - The directory path must be valid on the system runnign HAL, not the system running the web browser ---Experiment specification- Metrics: PAR1 and PAR10 rely on HAL-measured CPU time; Reported PAR1 and PAR10 rely on algorithm-reported CPU time | |||||||
View topic | History: r16 < r15 < r14 < r13 | More topic actions...
Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? Send feedback