Example: x86 Page Table (32-bits)
This example models an x86 page table, an in-memory data structure.
Description
The following figure depicts the page table format from the Intel 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual.
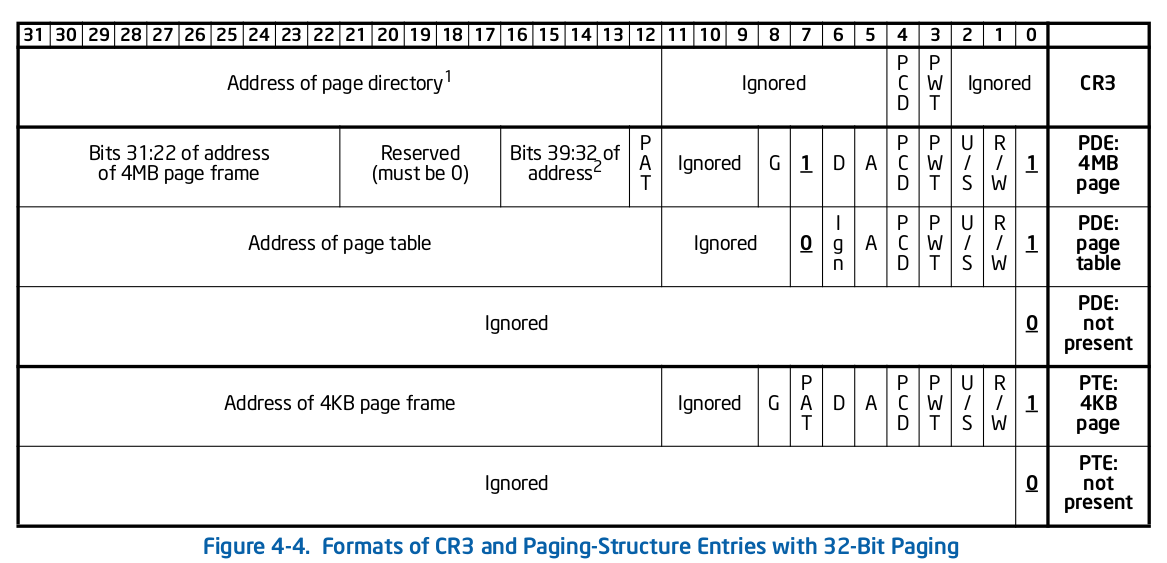
CR3
| Bit Positions | Contents |
|---|---|
| 3 (PWT) | Set write-through |
| 4 (PCD) | Set cache disabled |
| 31:12 (Addr) | Address of page directory |
Page Directory (Normal)
| Bit Positions | Contents |
|---|---|
| 0 (P) | Present; must be 1 to map. |
| 1 (R/W) | If 1 writable |
| 2 (U/S) | If 1 user mode access allowed |
| 3 (PWT) | Set write-through |
| 4 (PCD) | Set cache disabled |
| 5 (A) | Access flag |
| 7 (PS) | Page select. Must be 0 |
| 31:12 (Addr) | Address of page table |
Page Directory (Super Page Mapping)
| Bit Positions | Contents |
|---|---|
| 0 (P) | Present; must be 1 to map. |
| 1 (R/W) | If 1 writable |
| 2 (U/S) | If 1 user mode access allowed |
| 3 (PWT) | Set write-through |
| 4 (PCD) | Set cache disabled |
| 5 (A) | Access flag |
| 6 (D) | Dirty flag |
| 7 (PS) | Page select. Must be 1 |
| 31:22 (Addr) | Address of frame |
Page Table
The page table maps an aligned 4k page in memory.
| Bit Positions | Contents |
|---|---|
| 0 (P) | Present; must be 1 to map. |
| 1 (R/W) | If 1 writable |
| 2 (U/S) | If 1 user mode access allowed |
| 3 (PWT) | Set write-through |
| 4 (PCD) | Set cache disabled |
| 5 (A) | Access flag |
| 6 (D) | Dirty flag |
| 31:12 (Addr) | Address of frame |
Unit Specification (Page Table)
Editable field to fill in the spec. Does not save
unit X86PageTable(..) {
..
}