Third edition of Artificial Intelligence: foundations of computational agents, Cambridge University Press, 2023 is now available (including the full text).
10.2.2 Extensive Form of a Game
Whereas the normal form of a game represents controllers as single units, it if often more natural to specify the unfolding of a game through time. The extensive form of a game is an extension of a single-agent decision tree. We first give a definition that assumes the game is fully observable (called perfect information in game theory).
A perfect information game in extensive form or a game tree is a finite tree where the nodes are states and the arcs correspond to actions by the agents. In particular:
- Each internal node is labeled with an agent (or with nature). The agent is said to control the node.
- Each arc out of a node labeled with agent i corresponds to an action for agent i.
- Each internal node labeled with nature has a probability distribution over its children.
- The leaves represent final outcomes and are labeled with a utility for each agent.
The extensive form of a game specifies a particular unfolding of the game. Each path to a leaf, called a run, specifies one particular way that the game could proceed depending on the choices of the agents and nature.
A pure strategy for agent i is a function from nodes controlled by agent i into actions. That is, a pure strategy selects a child for each node that agent i controls. A strategy profile consists of a strategy for each agent.
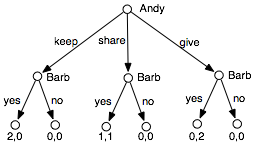
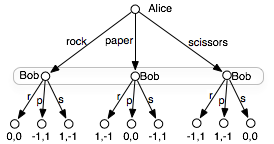
The extensive form of the sharing game is shown in Figure 10.2. Andy has 3 strategies. Barb has 8 pure strategies; one for each combination of assignments to the nodes she controls. As a result, there are 24 strategy profiles.
Given a strategy profile, each node has a utility for each agent. The utility for an agent at a node is defined recursively from the bottom up:
- The utility for each agent at a leaf is given as part of the leaf.
- The utility for agent j of a node controlled by agent i is the utility for agent j of the child node that is selected by agent i's strategy.
- The utility for agent i for a node controlled by nature is the expected value of the utility for agent i of the children. That is, ui(n)=∑c P(c)ui(c), where the sum is over the children c of node n, and P(c) is the probability that nature will choose child c.
The preceding definition of the extensive form of a game assumes that the agents can observe the state of the world (i.e., they know what node they are at each step). This means that the state of the game must be fully observable. In a partially observable game or an imperfect information game, the agents do not necessarily know the state of the game. To model these games in an extensive form, we introduce the notion of information sets. An information set is a set of nodes, all controlled by the same agent and all with the same set of available actions. The idea is that the agent cannot distinguish the elements of the information set. The agent only knows the game state is at one of the nodes of the information set, not which node. In a strategy, the agent chooses one action for each information set; the same action is carried out at each node in the information set. Thus, in the extensive form, a strategy specifies a function from information sets to actions.