Four papers by UBC Natural Language Processing group accepted at major conference
From multi-cultural inclusivity to a Chatbot for Canadian airline passengers, the topics are varied in four accepted papers for Dr. Vered Shwartz and her PhD students.
A variety of industries are starting to use Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT4, and are revolutionizing the way they conduct business. What that means for researchers in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) is that there is no end to the nuances of LLMs to study and refine, so as to ensure the models are being as true and helpful as possible to business and humankind.
For the UBC Computer Science department, research in NLP is on the rise. Four papers were recently accepted and presented by researchers at the 2024 Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) conference in November.
One paper, From Local Concepts to Universals: Evaluating the Multicultural Understanding of Vision-Language Models was authored by Mehar Bhatia (a previous UBC PhD student, now at McGill), Sahithya Ravi, Aditya Chinchure, EunJeong Hwang (all current UBC PhD students) and Vered Shwartz (Assistant Professor). The research presents a benchmark for evaluating Vision Language Models on their multicultural understanding.
EunJeong Hwang (UBC PhD student) also had a second paper published from her internship with Google which was accepted as an EMNLP Findings paper. Enhancing Incremental Summarization with Structured Representation was authored by EunJeong Hwang and and a team of Google Deepmind researchers. In the paper, they introduce ‘Chain-of-Key,’ which leverages LLM reasoning with structured representation.
A third paper published by Vered and co-authors was accepted to the main conference proceedings and is entitled Locating Information Gaps and Narrative Inconsistencies Across Languages: A Case Study of LGBT People Portrayals on Wikipedia. Authors are: Farhin Samir (UBC Linguistics), Chan Young Park, Anjalie Field, Vered Shwartz and Yulia Tsvetkov.
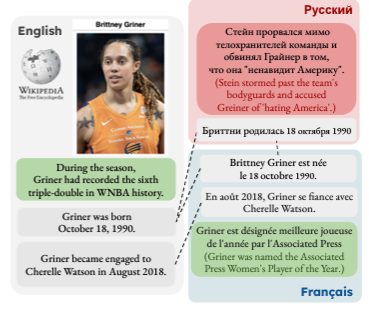
They introduce the InfoGap method—an efficient and reliable approach to locating information gaps and inconsistencies in articles at the fact level, across languages. They used the method to analyze LGBT people’s portrayals across Wikipedia pages in English, Russian, and French, and show differences in the selection of facts covered.
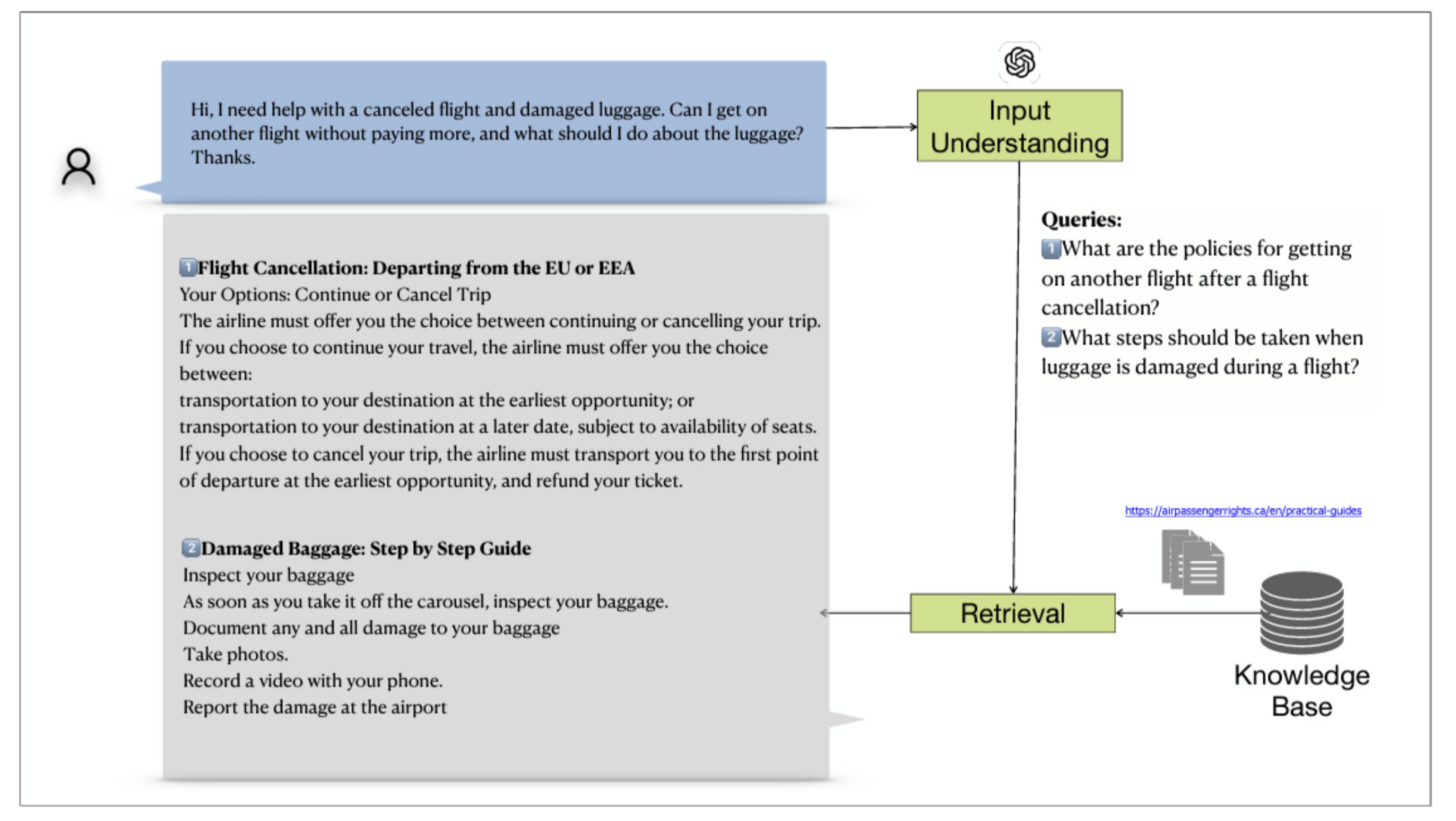
A fourth paper was accepted for a workshop, entitled Empowering Air Travelers: A Chatbot for Canadian Air Passenger Rights and was authored by Maksym Taranukhin, Sahithya Ravi (UBC PhD student), Gabor Lukacs, Evangelos Milios, and Vered Shwartz. The researchers present a Chatbot to assist passengers and educate them on their rights related to experiencing flight delays, cancellations and other air travel issues.
Dr. Shwartz explained that the authors opted to have posters at the conference in order to gain more face-to-face interaction. “We had our choice of presentation type, and they all, except for the workshop paper, chose posters. It used to be more prestigious to have a talk, but now most EMNLP participants prefer posters because you get more exposure that way.”
Dr. Shwartz states she is pleased with the showing, “I'm proud of the work we've been doing, and this is definitely one of the top tier NLP conferences in which to present.” She was also surprised at the variety of participants attending from other industries expressing interest in using NLP and learning more. “Everyone is using LLMs these days but many people don’t reach out to the experts. Some industries are just beginning to realize they can’t necessarily always count on off-the-shelf LLM-based solutions, and when accuracy and liability are crucial, it’s best to talk to NLP experts for custom solutions.”